Essential SQL Queries and Techniques Every Data Professional Should Know
Mastering SQL Fundamentals for Data Analysis
Mastering SQL fundamentals forms the cornerstone of effective data analysis. Data professionals must excel at complex joins, window functions, and subquery optimization to extract meaningful insights from enterprise datasets. Understanding query execution plans and index utilization ensures optimal performance across large-scale analytical workloads.
Advanced JOIN Techniques
Multi-table Relationships
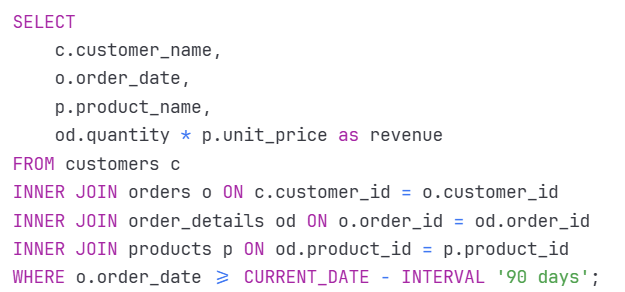
- Self-Joins for Hierarchical Data: Essential for organizational structures and product categories, self-joins enable recursive data analysis without complex programming logic.
Window Functions Mastery
Analytical window functions revolutionize data analysis capabilities, enabling sophisticated
calculations without GROUP BY limitations.
Running Totals and Moving Averages
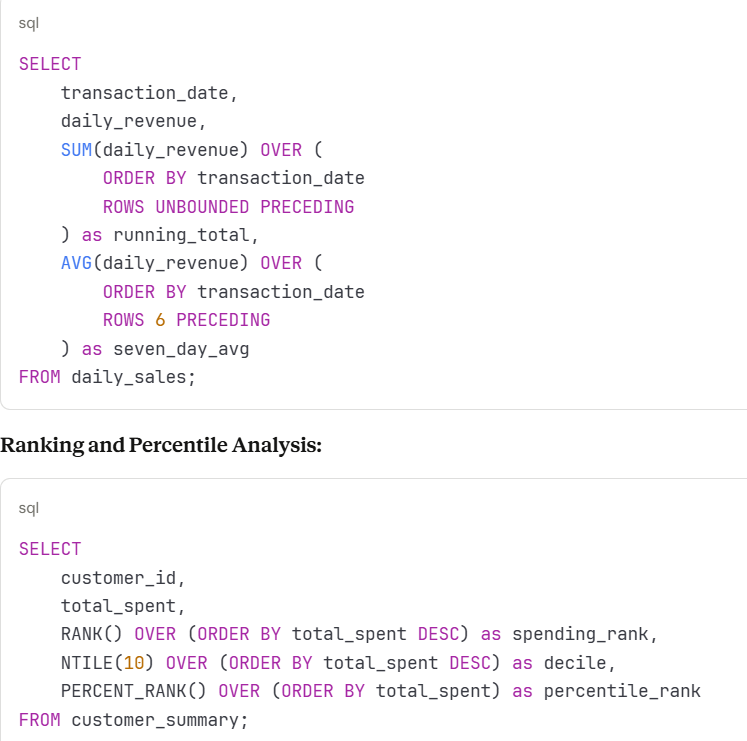
These techniques allow tracking trends over time within partitions of data.
Advanced Aggregation Techniques
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) improve query readability and enable recursive operations for complex business logic.
Cohort Analysis Implementation
WITH first_purchase AS (
SELECT
customer_id,
MIN(order_date) AS first_order_date
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id
),
monthly_activity AS (
SELECT
fp.customer_id,
fp.first_order_date,
o.order_date,
DATE_TRUNC('month', fp.first_order_date) AS cohort_month,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM AGE(o.order_date, fp.first_order_date)) AS period_number
FROM first_purchase fp
JOIN orders o ON fp.customer_id = o.customer_id
)
SELECT
cohort_month,
period_number,
COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) AS customers,
COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) /
FIRST_VALUE(COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id)) OVER (
PARTITION BY cohort_month ORDER BY period_number
) * 100 AS retention_rate
FROM monthly_activity
GROUP BY cohort_month, period_number;
Performance Optimization Strategies
Query Performance Tuning
- Implement covering indexes for frequently accessed columns
- Utilize
EXPLAIN ANALYZEfor execution plan optimization - Apply query hints judiciously for complex analytical workloads
- Leverage materialized views for expensive aggregations
Data Type Optimization
Choose appropriate data types minimizing storage overhead while maintaining precision.
Use DECIMAL for financial calculations,
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE for global applications,
and UUID for distributed systems.
Modern SQL Features
- JSON Processing: Contemporary databases support semi-structured data analysis through native JSON functions, enabling flexible schema evolution without sacrificing performance.
- Temporal Data Analysis: Master date arithmetic, time zone conversions, and interval calculations for comprehensive time-series analytics essential in business intelligence.
Best Practices for Enterprise Environments
- Implement parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities.
- Establish naming conventions for tables, columns, and constraints for maintainable codebases.
- Utilize database documentation and data dictionaries for collaborative development.
- Code Review Standards: Enforce peer review for production SQL deployments, implement version control for schema changes, and maintain rollback procedures for critical updates.
These essential SQL techniques enable data professionals to extract actionable insights efficiently while maintaining query performance and data integrity across enterprise analytical platforms.