ETL Explained: How Data Journeys from Source to Insight
ETL Explained: Turning Messy Data into a Strategic Business Asset
For the current data-driven world, businesses are swimming in information — from sales transactions and customer clicks to supply-chain logs. Raw data is often chaotic, inconsistent, and siloed. The answer to turning this mess into value is a fundamental process called ETL: Extract, Transform, Load.
What is ETL?
ETL is a three-step data integration process that acts as the backbone for data warehousing and business intelligence. It’s the behind-the-scenes workhorse that prepares raw data for analysis. Below we break down each stage of the pipeline.
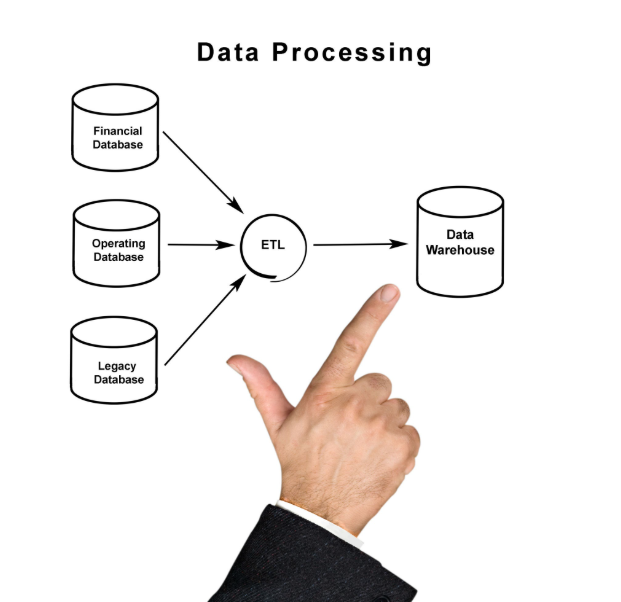
The Three Stages of the Data Pipeline
1. Extract (E)
The journey begins by pulling data from its various sources. These sources can be diverse, including:
- Relational databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL
- CRM systems like Salesforce
- Flat files such as CSVs or JSON logs
- APIs from third-party services
The goal of this stage is to gather all necessary raw materials from their original locations.
2. Transform (T)
This is where the real magic happens. Raw data is rarely ready for analysis; the transform stage cleans, standardizes, and restructures data to ensure quality and consistency. Common transformations include:
- Cleaning: Removing duplicates and handling missing values (nulls).
- Standardizing: Normalizing date formats (e.g., MM-DD-YYYY → YYYY-MM-DD) and units.
- Enriching: Combining data sources (for example, adding customer demographics to sales records).
- Aggregating: Summarizing data (e.g., calculating total monthly sales from transaction logs).
This step ensures the data loaded into the final system is reliable and uniform.
3. Load (L)
In the final stage, the transformed data is loaded into a target destination—typically a data warehouse or data lake—optimized for analysis and reporting. Once loaded, the data becomes available for BI tools, data scientists, and analysts to query and visualize.
Case Study: A U.S. Retailer Optimizes Inventory with ETL
A leading nationwide retailer in the USA faced a classic data challenge: point-of-sale (POS) sales data, warehouse inventory data, and online customer feedback were trapped in separate systems, preventing a unified view of operations.
How the ETL pipeline was implemented
- Extract: Data was pulled nightly from POS, WMS, and customer feedback systems.
- Transform: Product SKUs were standardized, customer records cleaned, and sales figures joined with real-time inventory levels to create a cohesive dataset.
- Load: Consolidated data was loaded into a cloud data warehouse for analytics and reporting.
Outcome
The analytics team built dashboards correlating regional sales trends with inventory and sentiment. They identified overstocked and understocked products by region, optimized the supply chain, reduced holding costs, and increased sales by ensuring popular products were available where demand was highest.
Why ETL Matters
ETL isn't just a technical acronym; it's a foundational business process that transforms raw, unusable data into strategic assets that drive growth and efficiency. When implemented well, ETL enables better decisions, faster insights, and measurable financial benefits.